Thursday, March 20, 2014
How to Creating Your Facebook Profile
On Facebook, you are represented by your Profile—a page that communicates who you are. Your Profile can include information about your age, gender, background, interests, hobbies, relationships, and more—or none of these things at all. You'll decide how much you want to share about yourself on your Profile.
In this lesson, you'll learn how to add details to your Profile and choose privacy levels for the information you share. We'll also talk about how to use the View As Tool and explain how Likes can affect your Profile.
Creating Your Facebook Profile
Controlling Privacy on Your Profile
Before you add any information to your Profile, you should think about how that information will affect how people think about you. This doesn't just apply to negative or embarrassing information—you may not want to share any information you would be uncomfortable sharing with every person in your life.
As with other things you share on Facebook, you can use the audience selector to set privacy levels for each part of your Profile. However, keep in mind that the only way to be certain that your information will stay private is to not share it at all. If you'd be deeply embarrassed about details of your personal life becoming public, you shouldn't share that information on your Profile.
Creating Your Profile
There are two parts of your Profile: the Profile page and the About page. The Profile page appears whenever you or anyone else navigates to your Profile, and also includes your Profile picture, Cover photo, and Timeline. The About page includes the personal details and information you've shared.
To edit the information on your About page, navigate to your Profile page and then select Update Info.
Accessing your information page
*Click the buttons in the interactive below to learn more about adding information to your Profile and setting privacy levels for the details you share.
*You can learn how to add your Profile picture, cover photo, and more by reviewing our lesson on Getting Started with Facebook
Checking Your Profile Privacy
Once you've chosen your Profile's Privacy Settings, you should double-check your Profile to ensure you're not sharing more than you intended. The View As Tool makes this easy, allowing you to see what other people see when they view your Profile.
To Use the View As Tool:
1. Locate and select the Advanced Settings Gear on your Profile page, then select View As... from the drop-down menu.
Clicking View As...
2. A preview of your Profile page as it would look to someone who is not your Friend on Facebook will appear. You can also click View as Specific Person to see your Profile as it would look to specific Friends.
Viewing your Profile page as it would appear to the public
3. Review your Profile to make sure you can't see any information you'd rather keep private. When you're finished, click the X in the top-left corner of the page to return to your Profile.
Exiting View As...
Understanding Likes and Interests
When you add details to the Information page of your Profile, you can include information about your favorite music, movies, hobbies, and more, which are known as Likes. Any organization or celebrity you've Liked on Facebook will also appear here. Your Likes are represented by a small thumbnail image on the Likes section of your Profile information page. Each of these images is actually a link to a Fan page or Topic page about a particular Like or Interest.
Linked interests on a Profile
The information you share about Likes is very valuable to Facebook. Facebook and other sites can use it to market, advertise, and make suggestions to you based on your interests. While these are common advertising practices across the web that some people do not mind, many others are simply unaware of them altogether. The examples below list a few ways Facebook uses this information. If you are uncomfortable with any of these practices, you may want to be more careful about what you Like on Facebook.
Here are a few of the places you might see your Likes and Interests around Facebook:
*Your Likes and Interests may be included in your Profile when people conduct a public search for you. If you use Facebook for professional networking, you may want to make sure your interests don't reflect poorly on you.
Public Search results showing Likes and Interests
*Anything you Like can be posted to your Timeline or to your Friends' News Feeds for your Friends to see. This can be mildly embarrassing or very revealing, depending on your interests.
Revealing interests posted in Facebook's News Feed
*Posts from the Fan Pages of your Likes and Interests will appear in your News Feed.
Promotional post based on Likes and Interests
Deactivating Your Facebook Account
Deactivating Your Account
Not enjoying Facebook as much as you thought you would? If you decide Facebook isn't the place for you, it's easy to deactivate your account in a few simple steps.
To Deactivate Your Account:
When you deactivate your Facebook account, it will become invisible to you and everyone else on Facebook. Once your account is deactivated, you will no longer be able to access your posts, photos, messages, and other information. Read more...........
Article Source: http://www.gcflearnfree.org
Monday, August 19, 2013
How to Create a Gmail Account
1. Go to the Gmail homepage
2. Click “create an account. “
3. Fill in your real information.
4. Fill in the captchas, and agree to the terms of service.
5. Click Next Step.
6. Add a profile photo if you would like by clicking add
profile photo. If you would like to skip that step, click Next Step.
7. Click “continue to Gmail. “
8. Now complete your Gmail account.
C.c. CD-ROM-Compact Disc-Read-Only Memory (What Is This)
CD-ROM stands for compact disc read only
memory. A CD-ROM can store about 700MB
of data. That is enough to hold about 3000000 text pages. Because CDs are inexpensive to produce yet
provide access to so much storage, CD-ROM
has become the medium of choice for publishing multimedia applications.
CDS bring music, literature, and video
to your desktop, allow you to share animation, multimedia presentations, and
software applications, and introduce you to the latest 3D games, medical
journals, and reference materials. For years, computer systems have come
standard with at least one CD-ROM
drive. However, today’s technological advances offer other, more versatile CD options to consumers than the
traditional read-only CD-ROM drive.
Advanced options include CD-Recorder
drives that can write or record data only once to a CD, CD-Re-writer drives
that can write, erase, and rewrite data to a CD, or faster and more flexible CD-ROM drives that can also read media produced in a CD-R or CD-RW drive.
The speed of the CD-ROM
is measured in how many thousands of characters it can read per second. The
first CD-ROM drives could transfer
data at a rate of 140K per second. Double
speed CD-ROM drives can transfer
data at twice that speed, or 300K per second. Now 42x are also available.
Multisession refers to a CD-ROM
drive that can play back CDs
that have been recorded on more than once.
Friday, August 16, 2013
C.H. Hard Drive (What Is This)
The Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is the main
secondary storage device used to permanently store information and consists of
one or more magnetic disks contained in a box. An important function of a HDD is to store program files. When you
purchase a new program, you need to install the program files to the HDD before you can run the program.
Most programs will not work unless they are properly installed on the hard
drive.
Speed –disk
can spin much faster, thousands of RPM
(revolution per minute). As a result of higher recording density and faster
spinning, hard drive can write and retrieve information much faster.
The hard
drive is connected to a disk controller with a cable. The hard drive can be
connected by Enhanced integrated Drive Electronics (EIDE), and Small Computer System Interface (SCSI), pronounced “scuzzy”, connections.
EIDE is an improvement in transfer speed
of the IDE, since it is typically
connected to the system motherboard. The EIDE interface supports up to four
drives, a master and slave on each of two channels. The intermediate PIO (Programmed or Processor I/O) modes and DMA (Direct Memory Access) modes used by EIDE and FAST-ATA are
big performance boosters. Ultra DMA (also
known as Ultra ATA) data transfer of
33 MB/S (megabytes per second) or 44MB/S or 100MB/S.
SCSI is a high-end controller system,
where the units are connected to a special controller, which is rather
expensive.
New Hard disk
has more than 40GB (Gigabytes) of
capacity and Ultra ATA/100 and 7200rpm (revolution per minute) spindle
speed.
Sunday, August 4, 2013
Type of stocks
2. brown stock
Methods for white vegetable stock
Ingredients -: 100gr – onion
100gr – carrot
100gr – leeks
100gr – celery
(stem)
11/2 liter
– water
Method
1. Place all ingredients in cupper
saucepan. Add the water. Bring to the boil
2. Allow to simmer for approximately one
hour.
3. Skim if necessary, strain and use.
Methods for brown vegetable stock
Ingredients -: 100gr – onion
100gr – carrot
100gr – leeks (whit
pat)
100gr – celery (stem)
11/2
liter – water
60 ml - oil
50 ml - tomato
6 - Pepper coin
Method
1. Fry the onion, carrot, celery and
leeks in oil until golden brown.
2. Drain the vegetable, place in to a
suitable saucepan.
3. Add all the ingredients cover with
water.
4. Bring to the boil.
5. Simmer gently for one hour.
6. Skim if necessary and use.
Thursday, July 18, 2013
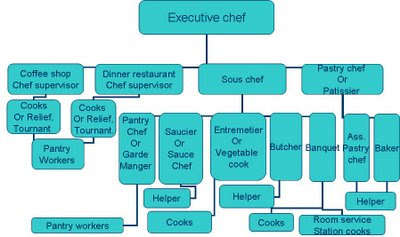
Kitchen Department (What is Responsibilities?)
Responsibilities and Duties of
Executive Chef
1. Maintain the hygiene food
2. Staffing recruitment – roistering
3. Menu planning
4. Costing
5. Ordering
6. Controlling
Responsibilities of Sous Chef
1. Assistance to the executive chef
Responsibilities of pastry chef
1. Maintain a high standard in the
pastry section
2. Staffing, roistering, controlling
3. Ordering
4. Costing
5. Controlling the pastry section
Responsibilities of Chef De Party
1. Report to the executive chef
2. Maintain the standard or their
perfidious section.
3. Controlling
4. Ordering
5. Lesion with the other section the
kitchen
Sunday, July 7, 2013
Types of Menus and Tariff Structures
1. Breakfast menu
2. Lunch menu
3. Dinner menu
4. Set menu
5. A ’la carte
6. Kids menu
7. Vegetables menu
8. Snack menu
R/o – room
only
B/b – bed
and breakfast = room + breakfast
H/b – half
board = room + breakfast + dinner
F/b – full
board = room + breakfast + lunch + dinner
Types Of
breakfast
1.
Continental
breakfast
* Start -
Fresh fruits or fruit juice
* Toasted
– jam, marmalade, butter
* Finish - Tea
and coffee
2..
English
breakfast
1.
Start
- Fresh fruit or fruit juice
2.
Toasted
– butter, jam, marmalade
3.
Eggs
(fried egg, omelet, poaching, boil)
4.
Bacon,
sausage
5.
Finish
- Tea and coffee
1.
American
breakfast
1.
Start - Fresh fruits or fruit juice
2.
Toasted
– butter, jam , marmalade
3.
Egg,
bacon, sauce
4.
Porrage
5.
Mini
stark or fish stark
6.
Finish -Tea and coffee













.jpg)

























































.jpg)






















